BackgroundService 사용하여 Windows 서비스 만들기
.NET Framework 개발자는 Windows 서비스 앱에 익숙할 것입니다. .NET Core 및 .NET 5 이상 이전에는 .NET Framework에 의존했던 개발자가 백그라운드 작업을 수행하거나 장기 실행 프로세스를 실행하는 Windows 서비스를 만들 수 있습니다. 이 기능은 계속 사용할 수 있으며 Windows 서비스로 실행되는 작업자 서비스를 만들 수 있습니다.
이 자습서에서는 다음 방법을 알아봅니다.
- .NET 작업자 앱을 단일 파일 실행 파일로 게시합니다.
- Windows 서비스를 만듭니다.
-
BackgroundService앱을 Windows 서비스로 만듭니다. - Windows 서비스를 시작하고 중지합니다.
- 이벤트 로그를 봅니다.
- Windows 서비스를 삭제합니다.
팁
모든 ‘.NET 작업자’ 예제 소스 코드는 샘플 브라우저에서 다운로드할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 코드 샘플 찾아보기: .NET작업자를 참조하세요.
중요하다
.NET SDK를 설치하면 Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Worker 및 작업자 템플릿도 설치됩니다. 즉, .NET SDK를 설치한 후 dotnet new worker 명령을 사용하여 새 작업자를 만들 수 있습니다. Visual Studio를 사용하는 경우 선택적 ASP.NET 및 웹 개발 워크로드가 설치될 때까지 템플릿이 숨겨집니다.
필수 구성 요소
- .NET 8.0 SDK 버전 이상
- 윈도우 운영 체제
- .NET IDE(통합 개발 환경)
새 프로젝트 만들기
Visual Studio를 사용하여 새 작업자 서비스 프로젝트를 만들려면 파일>새>Project...선택합니다. 새 프로젝트 만들기 대화 상자에서 "작업자 서비스"를 검색하고 작업자 서비스 템플릿을 선택합니다. .NET CLI를 사용하려는 경우 작업 디렉터리에서 즐겨 찾는 터미널을 엽니다.
dotnet new 명령을 실행하고 <Project.Name> 원하는 프로젝트 이름으로 바꿉다.
dotnet new worker --name <Project.Name>
.NET CLI 새 작업자 서비스 프로젝트 명령에 대한 자세한 내용은 dotnet 새 작업자참조하세요.
팁
Visual Studio Code를 사용하는 경우 통합 터미널에서 .NET CLI 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 Visual Studio Code: 통합 터미널참조하세요.
NuGet 패키지 설치
.NET IHostedService 구현에서 네이티브 Windows 서비스와 상호 작용하려면 Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices NuGet 패키지설치해야 합니다.
Visual Studio에서 설치하려면 NuGet 패키지 관리... 대화 상자를 사용합니다. "Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices"를 검색하고 설치합니다. .NET CLI를 사용하려는 경우 dotnet add package 명령을 실행합니다.
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices
.NET CLI 패키지 추가 명령에 대한 자세한 내용은 dotnet add package참조하세요.
패키지를 성공적으로 추가한 후 프로젝트 파일에는 이제 다음 패키지 참조가 포함되어야 합니다.
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting" Version="9.0.3" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices" Version="9.0.3" />
</ItemGroup>
프로젝트 파일 업데이트
이 작업자 프로젝트는 C#의nullable 참조 형식을 사용합니다. 전체 프로젝트에 대해 사용하도록 설정하려면 프로젝트 파일을 적절하게 업데이트합니다.
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Worker">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0-windows</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>true</ImplicitUsings>
<RootNamespace>App.WindowsService</RootNamespace>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting" Version="9.0.3" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices" Version="9.0.3" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
위의 프로젝트 파일 변경 내용은 <Nullable>enable<Nullable> 노드를 추가합니다. 자세한 내용은 nullable 컨텍스트 설정을 참조하세요.
서비스 만들기
JokeService.cs프로젝트에 새 클래스를 추가하고 해당 내용을 다음 C# 코드로 바꿉니다.
namespace App.WindowsService;
public sealed class JokeService
{
public string GetJoke()
{
Joke joke = _jokes.ElementAt(
Random.Shared.Next(_jokes.Count));
return $"{joke.Setup}{Environment.NewLine}{joke.Punchline}";
}
// Programming jokes borrowed from:
// https://github.com/eklavyadev/karljoke/blob/main/source/jokes.json
private readonly HashSet<Joke> _jokes = new()
{
new Joke("What's the best thing about a Boolean?", "Even if you're wrong, you're only off by a bit."),
new Joke("What's the object-oriented way to become wealthy?", "Inheritance"),
new Joke("Why did the programmer quit their job?", "Because they didn't get arrays."),
new Joke("Why do programmers always mix up Halloween and Christmas?", "Because Oct 31 == Dec 25"),
new Joke("How many programmers does it take to change a lightbulb?", "None that's a hardware problem"),
new Joke("If you put a million monkeys at a million keyboards, one of them will eventually write a Java program", "the rest of them will write Perl"),
new Joke("['hip', 'hip']", "(hip hip array)"),
new Joke("To understand what recursion is...", "You must first understand what recursion is"),
new Joke("There are 10 types of people in this world...", "Those who understand binary and those who don't"),
new Joke("Which song would an exception sing?", "Can't catch me - Avicii"),
new Joke("Why do Java programmers wear glasses?", "Because they don't C#"),
new Joke("How do you check if a webpage is HTML5?", "Try it out on Internet Explorer"),
new Joke("A user interface is like a joke.", "If you have to explain it then it is not that good."),
new Joke("I was gonna tell you a joke about UDP...", "...but you might not get it."),
new Joke("The punchline often arrives before the set-up.", "Do you know the problem with UDP jokes?"),
new Joke("Why do C# and Java developers keep breaking their keyboards?", "Because they use a strongly typed language."),
new Joke("Knock-knock.", "A race condition. Who is there?"),
new Joke("What's the best part about TCP jokes?", "I get to keep telling them until you get them."),
new Joke("A programmer puts two glasses on their bedside table before going to sleep.", "A full one, in case they gets thirsty, and an empty one, in case they don’t."),
new Joke("There are 10 kinds of people in this world.", "Those who understand binary, those who don't, and those who weren't expecting a base 3 joke."),
new Joke("What did the router say to the doctor?", "It hurts when IP."),
new Joke("An IPv6 packet is walking out of the house.", "He goes nowhere."),
new Joke("3 SQL statements walk into a NoSQL bar. Soon, they walk out", "They couldn't find a table.")
};
}
readonly record struct Joke(string Setup, string Punchline);
위의 농담 서비스 소스 코드는 단일 기능인 GetJoke 메서드를 노출합니다. 임의 프로그래밍 농담을 나타내는 string 반환 메서드입니다. 클래스 스코프 _jokes 필드는 농담 목록을 저장하는 데 사용됩니다. 임의 농담이 목록에서 선택되어 반환됩니다.
Worker 클래스 다시 쓰기
템플릿의 기존 Worker 다음 C# 코드로 바꾸고 파일 이름을 WindowsBackgroundService.cs바꿉니다.
namespace App.WindowsService;
public sealed class WindowsBackgroundService(
JokeService jokeService,
ILogger<WindowsBackgroundService> logger) : BackgroundService
{
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
try
{
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
string joke = jokeService.GetJoke();
logger.LogWarning("{Joke}", joke);
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1), stoppingToken);
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// When the stopping token is canceled, for example, a call made from services.msc,
// we shouldn't exit with a non-zero exit code. In other words, this is expected...
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger.LogError(ex, "{Message}", ex.Message);
// Terminates this process and returns an exit code to the operating system.
// This is required to avoid the 'BackgroundServiceExceptionBehavior', which
// performs one of two scenarios:
// 1. When set to "Ignore": will do nothing at all, errors cause zombie services.
// 2. When set to "StopHost": will cleanly stop the host, and log errors.
//
// In order for the Windows Service Management system to leverage configured
// recovery options, we need to terminate the process with a non-zero exit code.
Environment.Exit(1);
}
}
}
앞의 코드에서 JokeServiceILogger함께 삽입됩니다. 둘 다 클래스에서 필드로 사용할 수 있습니다.
ExecuteAsync 방법에서 농담 서비스는 농담을 요청하고 로거에게 씁니다. 이 경우 로거는 Windows 이벤트 로그 Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.EventLog.EventLogLoggerProvider의해 구현됩니다. 로그는 기록되며 이벤트 뷰어에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
메모
기본적으로 이벤트 로그 심각도는 Warning. 이를 구성할 수 있지만 데모용으로 WindowsBackgroundServiceLogWarning 확장 메서드를 사용하여 로그합니다.
EventLog 수준을 구체적으로 대상으로 지정하려면 appsettings에 항목을 추가합니다. {Environment}.json또는 EventLogSettings.Filter 값을 제공합니다.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
},
"EventLog": {
"SourceName": "The Joke Service",
"LogName": "Application",
"LogLevel": {
"Microsoft": "Information",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
}
}
}
로그 수준을 구성하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 .NET의 로깅 공급자: Windows EventLog구성을 참조하세요.
Program 클래스 다시 쓰기
템플릿 Program.cs 파일 내용을 다음 C# 코드로 바꿉니다.
using App.WindowsService;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.EventLog;
HostApplicationBuilder builder = Host.CreateApplicationBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddWindowsService(options =>
{
options.ServiceName = ".NET Joke Service";
});
LoggerProviderOptions.RegisterProviderOptions<
EventLogSettings, EventLogLoggerProvider>(builder.Services);
builder.Services.AddSingleton<JokeService>();
builder.Services.AddHostedService<WindowsBackgroundService>();
IHost host = builder.Build();
host.Run();
AddWindowsService 확장 메서드는 Windows 서비스로 작동하도록 앱을 구성합니다. 서비스 이름이 ".NET Joke Service"로 설정되었습니다. 호스트된 서비스는 종속성 주입을 위해 등록됩니다.
서비스 등록에 대한 자세한 내용은 .NET 종속성 주입을 참조하세요.
앱 게시
.NET Worker Service 앱을 Windows 서비스로 만들려면 앱을 단일 파일 실행 파일로 게시하는 것이 좋습니다. 파일 시스템 주위에 있는 종속 파일이 없으므로 자체 포함 실행 파일이 있는 것은 오류가 적습니다. 그러나 Windows 서비스 제어 관리자가 대상으로 지정할 수 있는 *.exe 파일을 만드는 한 완벽하게 허용되는 다른 게시 형식을 선택할 수 있습니다.
중요하다
다른 게시 방법은 *.exe대신 *.dll 빌드하고 Windows Service Control Manager를 사용하여 게시된 앱을 설치할 때 .NET CLI에 위임하고 DLL을 전달하는 것입니다. 자세한 내용은 .NET CLI: dotnet 명령 참조하세요.
sc.exe create ".NET Joke Service" binpath= "C:\Path\To\dotnet.exe C:\Path\To\App.WindowsService.dll"
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Worker">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0-windows</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>true</ImplicitUsings>
<RootNamespace>App.WindowsService</RootNamespace>
<OutputType>exe</OutputType>
<PublishSingleFile Condition="'$(Configuration)' == 'Release'">true</PublishSingleFile>
<RuntimeIdentifier>win-x64</RuntimeIdentifier>
<PlatformTarget>x64</PlatformTarget>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting" Version="9.0.3" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices" Version="9.0.3" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
프로젝트 파일의 앞에 강조 표시된 줄은 다음 동작을 정의합니다.
-
<OutputType>exe</OutputType>: 콘솔 애플리케이션을 만듭니다. -
<PublishSingleFile Condition="'$(Configuration)' == 'Release'">true</PublishSingleFile>: 단일 파일 게시를 사용하도록 설정합니다. -
<RuntimeIdentifier>win-x64</RuntimeIdentifier>:win-x64의 RID를 지정합니다. -
<PlatformTarget>x64</PlatformTarget>: 64비트 대상 플랫폼 CPU를 지정합니다.
Visual Studio에서 앱을 게시하려면 유지되는 게시 프로필을 만들 수 있습니다. 게시 프로필은 XML 기반이며 .pubxml 파일 확장자를 가집니다. Visual Studio는 이 프로필을 사용하여 암시적으로 앱을 게시하는 반면, .NET CLI를 사용하는 경우 사용할 게시 프로필을 명시적으로 지정해야 합니다.
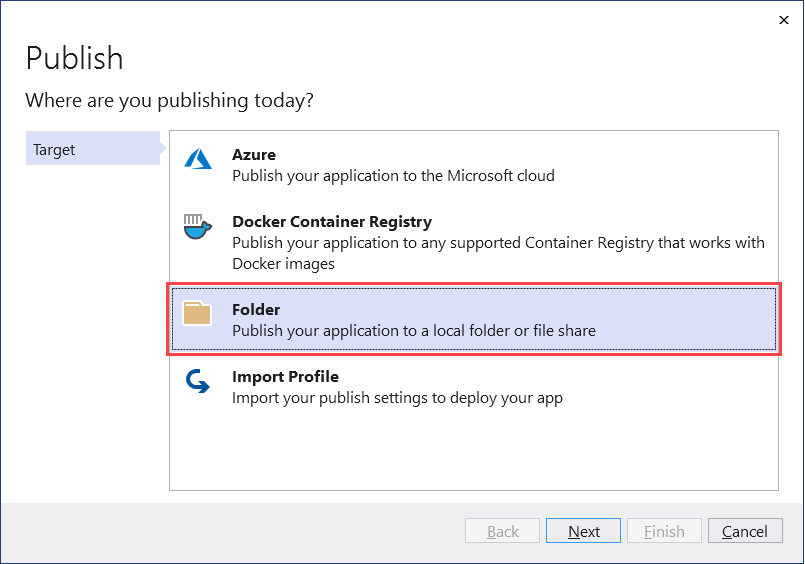
솔루션 탐색기에서 프로젝트를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭한 다음 게시를 선택합니다. 그런 다음, 게시 프로필 추가 을 선택하여 프로필을 만듭니다. 게시 대화 상자에서 폴더 를 대상로 선택합니다.
기본 위치를 그대로 두고, 마침을 선택합니다. 프로필이 만들어지면, 모든 설정을 표시선택한 후, 프로필 설정을확인하세요.
Visual Studio 프로필 설정
다음 설정이 지정되어 있는지 확인합니다.
- 배포 모드: 자체 포함
- 단일 파일생성: 체크됨
- ReadyToRun 컴파일을 사용하도록 설정: 선택됨
- 사용되지 않는 어셈블리 자르기(미리 보기): 선택 취소됨
마지막으로 게시선택합니다. 앱이 컴파일되고 결과 .exe 파일이 /publish 출력 디렉터리에 게시됩니다.
또는 .NET CLI를 사용하여 앱을 게시할 수 있습니다.
dotnet publish --output "C:\custom\publish\directory"
자세한 내용은 dotnet publish참조하세요.
중요하다
.NET 6에서는 <PublishSingleFile>true</PublishSingleFile> 설정으로 앱을 디버그하려고 하면 앱을 디버그할 수 없습니다. 자세한 내용은 'PublishSingleFile' .NET 6 앱디버깅할 때 CoreCLR에 연결할 수 없음을 참조하세요.
Windows 서비스 만들기
PowerShell 사용에 익숙하지 않고 서비스에 대한 설치 관리자를 만들려면 Windows 서비스 설치 관리자 만들기참조하세요. 그렇지 않은 경우 Windows 서비스를 만들려면 네이티브 Windows 서비스 제어 관리자(sc.exe) create 명령을 사용합니다. 관리자 권한으로 PowerShell을 실행합니다.
sc.exe create ".NET Joke Service" binpath= "C:\Path\To\App.WindowsService.exe"
팁
호스트 구성콘텐츠 루트를 변경해야 하는 경우 binpath지정할 때 명령줄 인수로 전달할 수 있습니다.
sc.exe create "Svc Name" binpath= "C:\Path\To\App.exe --contentRoot C:\Other\Path"
출력 메시지가 표시됩니다.
[SC] CreateService SUCCESS
자세한 내용은 sc.exe만들기를 참조하세요.
Windows 서비스 구성
서비스를 만든 후 필요에 따라 구성할 수 있습니다. 서비스 기본값이 괜찮으면 서비스 기능 확인 섹션으로 건너뜁니다.
Windows 서비스는 복구 구성 옵션을 제공합니다.
sc.exe qfailure "<Service Name>"(<Service Name> 서비스의 이름) 명령을 사용하여 현재 구성을 쿼리하여 현재 복구 구성 값을 읽을 수 있습니다.
sc qfailure ".NET Joke Service"
[SC] QueryServiceConfig2 SUCCESS
SERVICE_NAME: .NET Joke Service
RESET_PERIOD (in seconds) : 0
REBOOT_MESSAGE :
COMMAND_LINE :
이 명령은 아직 구성되지 않았기 때문에 기본값인 복구 구성을 출력합니다.

복구를 구성하려면 서비스의 이름인 <Service Name> 위치에 sc.exe failure "<Service Name>"를 사용합니다.
sc.exe failure ".NET Joke Service" reset= 0 actions= restart/60000/restart/60000/run/1000
[SC] ChangeServiceConfig2 SUCCESS
팁
복구 옵션을 구성하려면 터미널 세션을 관리자 권한으로 실행해야 합니다.
성공적으로 구성되면 sc.exe qfailure "<Service Name>" 명령을 사용하여 값을 다시 한 번 쿼리할 수 있습니다.
sc qfailure ".NET Joke Service"
[SC] QueryServiceConfig2 SUCCESS
SERVICE_NAME: .NET Joke Service
RESET_PERIOD (in seconds) : 0
REBOOT_MESSAGE :
COMMAND_LINE :
FAILURE_ACTIONS : RESTART -- Delay = 60000 milliseconds.
RESTART -- Delay = 60000 milliseconds.
RUN PROCESS -- Delay = 1000 milliseconds.
구성된 다시 시작 값이 표시됩니다.

서비스 복구 옵션 및 .NET BackgroundService 인스턴스
.NET 6에서는 새 호스팅 예외 처리 동작이 .NET에 추가되었습니다.
BackgroundServiceExceptionBehavior 열거형은 Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting 네임스페이스에 추가되었으며 예외가 throw된 경우 서비스의 동작을 지정하는 데 사용됩니다. 다음 표에서는 사용 가능한 옵션을 나열합니다.
| 선택 | 묘사 |
|---|---|
| Ignore |
BackgroundService에서 던져진 예외를 무시합니다. |
| StopHost | 처리되지 않은 예외가 던져질 때 IHost가 중지됩니다. |
.NET 6 이전의 기본 동작은 Ignore때문에 좀비 프로세스(아무 작업도 수행하지 않은 실행 프로세스)가 발생합니다. .NET 6에서는 기본 동작이 StopHost이며, 이는 예외가 throw될 때 호스트가 중지되는 결과를 초래합니다. 그러나 완전히 중지됩니다. 즉, Windows 서비스 관리 시스템이 서비스를 다시 시작하지 않습니다. 서비스를 다시 시작하도록 올바르게 허용하려면 0이 아닌 종료 코드로 Environment.Exit 호출할 수 있습니다. 강조 표시된 다음 catch 블록을 고려합니다.
namespace App.WindowsService;
public sealed class WindowsBackgroundService(
JokeService jokeService,
ILogger<WindowsBackgroundService> logger) : BackgroundService
{
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
try
{
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
string joke = jokeService.GetJoke();
logger.LogWarning("{Joke}", joke);
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1), stoppingToken);
}
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// When the stopping token is canceled, for example, a call made from services.msc,
// we shouldn't exit with a non-zero exit code. In other words, this is expected...
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger.LogError(ex, "{Message}", ex.Message);
// Terminates this process and returns an exit code to the operating system.
// This is required to avoid the 'BackgroundServiceExceptionBehavior', which
// performs one of two scenarios:
// 1. When set to "Ignore": will do nothing at all, errors cause zombie services.
// 2. When set to "StopHost": will cleanly stop the host, and log errors.
//
// In order for the Windows Service Management system to leverage configured
// recovery options, we need to terminate the process with a non-zero exit code.
Environment.Exit(1);
}
}
}
서비스 기능 확인
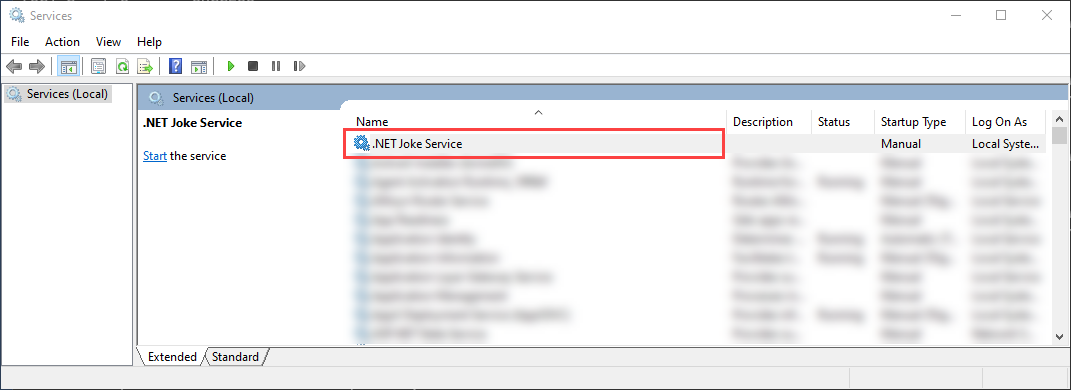
Windows 서비스로 만든 앱을 보려면 Services엽니다. Windows 키(또는 Ctrl + Esc)를 선택하고 "서비스"에서 검색합니다. Services 앱에서 해당 이름으로 서비스를 찾을 수 있어야 합니다.
중요하다
기본적으로 일반(비관리자) 사용자는 Windows 서비스를 관리할 수 없습니다. 이 앱이 예상대로 작동하는지 확인하려면 관리자 계정을 사용해야 합니다.
서비스가 예상대로 작동하는지 확인하려면 다음을 수행해야 합니다.
- 서비스 시작
- 로그 보기
- 서비스 중지
중요하다
애플리케이션을 디버그하려면 Windows Services 프로세스 내에서 현재 실행 중인 실행 파일을 디버그하려고 시도하지 있는지 확인합니다.

Windows 서비스 시작
Windows 서비스를 시작하려면 sc.exe start 명령을 사용합니다.
sc.exe start ".NET Joke Service"
다음과 유사한 출력이 표시됩니다.
SERVICE_NAME: .NET Joke Service
TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
STATE : 2 START_PENDING
(NOT_STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x7d0
PID : 37636
FLAGS
서비스 상태가 START_PENDING에서 실행 중인로 전환됩니다.
로그 보기
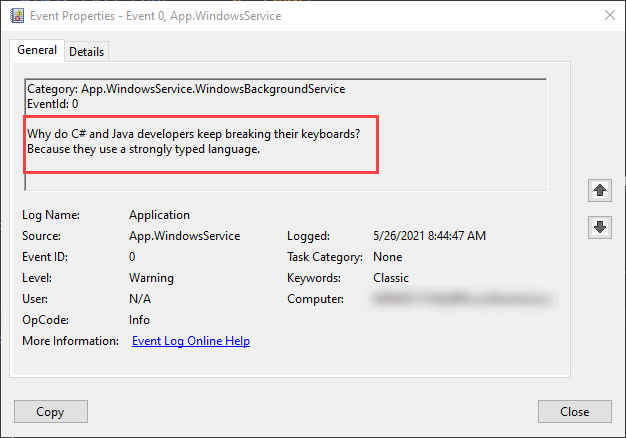
로그를 보려면 이벤트 뷰어엽니다. Windows 키(또는 Ctrl + Esc)를 선택하고 "Event Viewer"검색합니다.
이벤트 뷰어(로컬)>Windows 로그>애플리케이션 노드를 선택합니다. 앱 네임스페이스와 일치하는 원본을 포함한 경고 수준의 항목을 확인해야 합니다. 항목을 두 번 클릭하거나 마우스 오른쪽 단추를 클릭하고 이벤트 속성 선택하여 세부 정보를 봅니다.
이벤트 로그로그가 표시되면 서비스를 중지해야 합니다. 그것은 분당 한 번 임의의 농담을 기록하도록 설계되었습니다. 이는 의도적인 동작이지만 프로덕션 서비스에는 실용적이지 않습니다.
Windows 서비스 중지
Windows 서비스를 중지하려면 sc.exe stop 명령을 사용합니다.
sc.exe stop ".NET Joke Service"
다음과 유사한 출력이 표시됩니다.
SERVICE_NAME: .NET Joke Service
TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS
STATE : 3 STOP_PENDING
(STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN)
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0)
CHECKPOINT : 0x0
WAIT_HINT : 0x0
서비스 상태STOP_PENDING에서 중지된로 전환됩니다.
Windows 서비스 삭제
Windows 서비스를 삭제하려면 네이티브 Windows 서비스 제어 관리자(sc.exe) 삭제 명령을 사용합니다. 관리자 권한으로 PowerShell을 실행합니다.
중요하다
서비스가 중지됨 상태가 아니면 즉시 삭제되지 않습니다. delete 명령을 실행하기 전에 서비스가 중지되었는지 확인합니다.
sc.exe delete ".NET Joke Service"
출력 메시지가 표시됩니다.
[SC] DeleteService SUCCESS
자세한 내용은 sc.exe 삭제참조하세요.
참고
- Windows 서비스 설치 관리자 만들기
- .NET에서의 작업자 서비스
- 큐 서비스 만들기
-
BackgroundService내에서 범위가 지정된 서비스 사용 -
IHostedService인터페이스 구현
다음
.NET