Codec Merit
A partire da Windows 7, a un codec Media Foundation può essere assegnato un valore merito. Quando i codec vengono enumerati, i codec con meriti più elevati sono preferiti rispetto ai codec con meriti inferiori. I codec con qualsiasi valore di merito sono preferiti rispetto ai codec senza un merito assegnato. Per informazioni dettagliate sull'enumerazione codec, vedere MFTEnumEx.
I valori meriti vengono assegnati da Microsoft. Attualmente, solo i codec hardware sono idonei a ricevere un valore di merito. Il fornitore di codec viene rilasciato anche un certificato digitale, che viene usato per verificare il valore di merito del codec. Per ottenere un certificato, inviare una richiesta di posta elettronica a wmla@microsoft.com. Il processo per ottenere un certificato include la firma di una licenza e la fornitura di un set di file di informazioni a Microsoft.
Il merito del codec funziona come segue:
- Il fornitore di codec implementa uno dei seguenti elementi:
- Un mini-driver AVStream. Media Foundation fornisce un proxy standard MFT per i driver AVStream. Questa è l'opzione consigliata.
- Trasformazione Media Foundation (MFT) che funge da proxy per l'hardware. Per altre informazioni, vedere hardware MFT.
- Il valore di merito del codec viene archiviato nel Registro di sistema per una ricerca rapida.
- La funzione MFTEnumEx ordina i codec in ordine di merito. I codec con valori meriti vengono visualizzati nell'elenco dietro codec registrati localmente (vedere MFTRegisterLocal), ma prima di altri codec.
- Quando viene creato MFT, il merito del codec viene verificato usando l'API (OPM) di Output Protection Manager.
- Per un proxy MFT, il codec implementa l'interfacciaIOPMVideoOutput. Per un driver AVStream, il codec implementa il set di proprietà KSPROPSETID_OPMVideoOutput.
Il diagramma seguente mostra come viene verificato il merito in entrambi i casi:
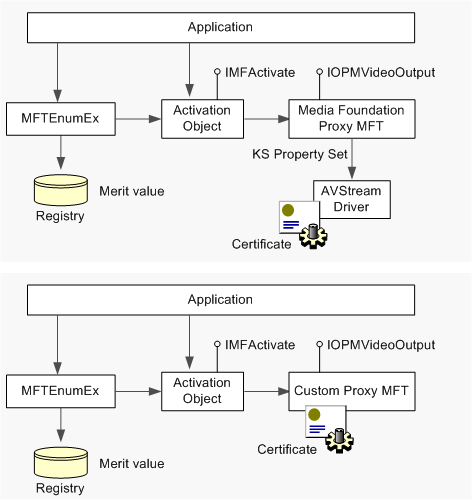
MFT proxy personalizzato
Se si fornisce un proxy MFT per il codec hardware, implementare il valore di merito del codec come indicato di seguito:
Implementare l'interfacciaIOPMVideoOutputin MFT. Il codice di esempio è illustrato nella sezione successiva di questo argomento.
Aggiungere l'attributo MFT_CODEC_MERIT_Attribute al Registro di sistema, come indicato di seguito:
- Chiamare MFCreateAttributes per creare un nuovo archivio attributi.
- Chiamare IMFAttributes::SetUINT32 per impostare l'attributo MFT_CODEC_MERIT_Attribute. Il valore dell'attributo è il merito assegnato al codec.
- Chiamare MFTRegister per registrare MFT. Passare l'archivio attributi nel parametro pAttributes.
L'applicazione chiama MFTEnumEx. Questa funzione restituisce una matrice di IMFActivate puntatori, uno per ogni codec che corrisponde ai criteri di enumerazione.
L'applicazione chiama IMFActivate::ActivateObject per creare MFT.
Il metodoActivateObjectchiama la funzioneMFGetMFTMeritper verificare il certificato e il valore di merito.
La funzione MFGetMFTMerit chiama IOPMVideoOutput::GetInformation e invia una richiesta di stato OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO. Questa richiesta di stato restituisce il valore di merito assegnato dal codec. Se questo valore non corrisponde al valore del Registro di sistema, ActivateObject potrebbe non riuscire.
Il codice seguente illustra come aggiungere il valore merit al Registro di sistema quando si registra MFT:
// Shows how to register an MFT with a merit value.
HRESULT RegisterMFTWithMerit()
{
// The following media types would apply to an H.264 decoder,
// and are used here as an example.
MFT_REGISTER_TYPE_INFO aDecoderInputTypes[] =
{
{ MFMediaType_Video, MFVideoFormat_H264 },
};
MFT_REGISTER_TYPE_INFO aDecoderOutputTypes[] =
{
{ MFMediaType_Video, MFVideoFormat_RGB32 }
};
// Create an attribute store to hold the merit attribute.
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
IMFAttributes *pAttributes = NULL;
hr = MFCreateAttributes(&pAttributes, 1);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
hr = pAttributes->SetUINT32(
MFT_CODEC_MERIT_Attribute,
DECODER_MERIT // Use the codec's assigned merit value.
);
}
// Register the decoder for MFTEnum(Ex).
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
hr = MFTRegister(
CLSID_MPEG1SampleDecoder, // CLSID
MFT_CATEGORY_VIDEO_DECODER, // Category
const_cast<LPWSTR>(SZ_DECODER_NAME), // Friendly name
0, // Flags
ARRAYSIZE(aDecoderInputTypes), // Number of input types
aDecoderInputTypes, // Input types
ARRAYSIZE(aDecoderOutputTypes), // Number of output types
aDecoderOutputTypes, // Output types
pAttributes // Attributes
);
}
SafeRelease(&pAttributes);
return hr;
}
Implementazione di IOPMVideoOutput per Codec Merit
Il codice seguente illustra come implementare IOPMVideoOutput per il merito del codec. Per una descrizione più generale dell'API OPM, vedere Output Protection Manager.
Nota
Il codice illustrato di seguito non presenta alcuna offuscamento o altri meccanismi di sicurezza. È progettato per mostrare l'implementazione di base dell'handshake OPM e della richiesta di stato.
Questo esempio presuppone che g_TestCert sia una matrice di byte contenente la catena di certificati del codec e g_PrivateKey sia una matrice di byte che contiene la chiave privata del certificato:
// Byte array that contains the codec's certificate.
const BYTE g_TestCert[] =
{
// ... (certificate not shown)
// Byte array that contains the private key from the certificate.
const BYTE g_PrivateKey[] =
{
// .... (key not shown)
Nel metodo IOPMVideoOutput::StartInitialization generare un numero casuale per l'handshake. Restituisce questo numero e il certificato al chiamante:
STDMETHODIMP CodecMerit::StartInitialization(
OPM_RANDOM_NUMBER *prnRandomNumber,
BYTE **ppbCertificate,
ULONG *pulCertificateLength
)
{
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
DWORD cbCertificate = sizeof(g_TestCert);
const BYTE *pCertificate = g_TestCert;
// Generate the random number for the OPM handshake.
hr = BCryptGenRandom(
NULL,
(PUCHAR)&m_RandomNumber,
sizeof(m_RandomNumber),
BCRYPT_USE_SYSTEM_PREFERRED_RNG
);
// Allocate the buffer to copy the certificate.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
*ppbCertificate = (PBYTE)CoTaskMemAlloc(cbCertificate);
if (*ppbCertificate == NULL)
{
hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY;
}
}
// Copy the certificate and the random number.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
*pulCertificateLength = cbCertificate;
CopyMemory(*ppbCertificate, pCertificate, cbCertificate);
*prnRandomNumber = m_RandomNumber;
}
return hr;
}
Il metodo IOPMVideoOutput::FinishInitialization completa l'handshake OPM:
STDMETHODIMP CodecMerit::FinishInitialization(
const OPM_ENCRYPTED_INITIALIZATION_PARAMETERS *pParameters
)
{
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
BCRYPT_ALG_HANDLE hAlg = NULL;
BCRYPT_KEY_HANDLE hKey = NULL;
BCRYPT_OAEP_PADDING_INFO paddingInfo = {0};
DWORD DecryptedLength = 0;
PBYTE pbDecryptedParams = NULL;
// The caller should pass the following structure in
// pParameters:
typedef struct {
GUID guidCOPPRandom; // Our random number.
GUID guidKDI; // AES signing key.
DWORD StatusSeqStart; // Status sequence number.
DWORD CommandSeqStart; // Command sequence number.
} InitParams;
paddingInfo.pszAlgId = BCRYPT_SHA512_ALGORITHM;
// Decrypt the input using the decoder's private key.
hr = BCryptOpenAlgorithmProvider(
&hAlg,
BCRYPT_RSA_ALGORITHM,
MS_PRIMITIVE_PROVIDER,
0
);
// Import the private key.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
hr = BCryptImportKeyPair(
hAlg,
NULL,
BCRYPT_RSAPRIVATE_BLOB,
&hKey,
(PUCHAR)g_PrivateKey, //pbData,
sizeof(g_PrivateKey), //cbData,
0
);
}
// Decrypt the input data.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
hr = BCryptDecrypt(
hKey,
(PBYTE)pParameters,
OPM_ENCRYPTED_INITIALIZATION_PARAMETERS_SIZE,
&paddingInfo,
NULL,
0,
NULL,
0,
&DecryptedLength,
BCRYPT_PAD_OAEP
);
}
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
pbDecryptedParams = new (std::nothrow) BYTE[DecryptedLength];
if (pbDecryptedParams == NULL)
{
hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY;
}
}
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
hr = BCryptDecrypt(
hKey,
(PBYTE)pParameters,
OPM_ENCRYPTED_INITIALIZATION_PARAMETERS_SIZE,
&paddingInfo,
NULL,
0,
pbDecryptedParams,
DecryptedLength,
&DecryptedLength,
BCRYPT_PAD_OAEP
);
}
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
InitParams *Params = (InitParams *)pbDecryptedParams;
// Check the random number.
if (0 != memcmp(&m_RandomNumber, &Params->guidCOPPRandom, sizeof(m_RandomNumber)))
{
hr = E_ACCESSDENIED;
}
else
{
// Save the key and the sequence numbers.
CopyMemory(m_AESKey.abRandomNumber, &Params->guidKDI, sizeof(m_AESKey));
m_StatusSequenceNumber = Params->StatusSeqStart;
m_CommandSequenceNumber = Params->CommandSeqStart;
}
}
// Clean up.
if (hKey)
{
BCryptDestroyKey(hKey);
}
if (hAlg)
{
BCryptCloseAlgorithmProvider(hAlg, 0);
}
delete [] pbDecryptedParams;
return hr;
}
Nel metodo IOPMVideoOutput::GetInformation implementare la richiesta di stato OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO. I dati di input sono una struttura OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_PARAMETERS che contiene il CLSID di MFT. I dati di output sono una struttura OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_INFORMATION che contiene il merito del codec.
STDMETHODIMP CodecMerit::GetInformation(
const OPM_GET_INFO_PARAMETERS *Parameters,
OPM_REQUESTED_INFORMATION *pRequest
)
{
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_PARAMETERS *CodecInfoParameters;
// Check the MAC.
OPM_OMAC Tag = { 0 };
hr = ComputeOMAC(
m_AESKey,
(PBYTE)Parameters + OPM_OMAC_SIZE,
sizeof(OPM_GET_INFO_PARAMETERS) - OPM_OMAC_SIZE,
&Tag
);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
if (0 != memcmp(Tag.abOMAC, &Parameters->omac, OPM_OMAC_SIZE))
{
hr = E_ACCESSDENIED;
}
}
// Validate the status sequence number. This must be consecutive
// from the previous sequence number.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
if (Parameters->ulSequenceNumber != m_StatusSequenceNumber++)
{
hr = E_ACCESSDENIED;
}
}
// Check the status request.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
if (Parameters->guidInformation != OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO)
{
hr = E_NOTIMPL;
}
}
// Check parameters.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
CodecInfoParameters = (OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_PARAMETERS *)Parameters->abParameters;
if (Parameters->cbParametersSize > OPM_GET_INFORMATION_PARAMETERS_SIZE ||
Parameters->cbParametersSize < sizeof(ULONG) ||
Parameters->cbParametersSize - sizeof(ULONG) != CodecInfoParameters->cbVerifier
)
{
hr = E_INVALIDARG;
}
}
// The input data should consist of the CLSID of the decoder.
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
CodecInfoParameters = (OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_PARAMETERS *)Parameters->abParameters;
if (CodecInfoParameters->cbVerifier != sizeof(CLSID) ||
0 != memcmp(&CLSID_MPEG1SampleDecoder,
CodecInfoParameters->Verifier,
CodecInfoParameters->cbVerifier))
{
hr = E_ACCESSDENIED;
}
}
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
// Now return the decoder merit to the caller.
ZeroMemory(pRequest, sizeof(OPM_REQUESTED_INFORMATION));
OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_INFORMATION *pInfo =
(OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_INFORMATION *)pRequest->abRequestedInformation;
pInfo->Merit = DECODER_MERIT;
pInfo->rnRandomNumber = Parameters->rnRandomNumber;
pRequest->cbRequestedInformationSize = sizeof(OPM_GET_CODEC_INFO_INFORMATION);
// Sign it with the key.
hr = ComputeOMAC(
m_AESKey,
(PBYTE)pRequest + OPM_OMAC_SIZE,
sizeof(OPM_REQUESTED_INFORMATION) - OPM_OMAC_SIZE,
&pRequest->omac
);
}
return hr;
}
Il metodoGetInformationdeve calcolare un codice MAC (Message Authentication Code) usando l'algoritmo OMAC-1; vedere Calcolo del valore OMAC-1.
Non è necessario supportare altre richieste di stato OPM.
I metodi IOPMVideoOutput::COPPCompatibleGetInformation e IOPMVideoOutput::Configure non sono necessari per il merito del codec, quindi questi metodi possono restituire E_NOTIMPL.
STDMETHODIMP CodecMerit::COPPCompatibleGetInformation(
const OPM_COPP_COMPATIBLE_GET_INFO_PARAMETERS *pParameters,
OPM_REQUESTED_INFORMATION *pRequestedInformation)
{
return E_NOTIMPL;
}
STDMETHODIMP CodecMerit::Configure(
const OPM_CONFIGURE_PARAMETERS *pParameters,
ULONG ulAdditionalParametersSize,
const BYTE *pbAdditionalParameters)
{
return E_NOTIMPL;
}
Argomenti correlati
-
scrittura di un MFT personalizzato