Events
Mar 17, 9 PM - Mar 21, 10 AM
Join the meetup series to build scalable AI solutions based on real-world use cases with fellow developers and experts.
Register nowThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
The recommended approach to authenticate an Azure-hosted app to other Azure resources is to use a managed identity. This approach is supported for most Azure services, including apps hosted on Azure App Service, Azure Container Apps, and Azure Virtual Machines. Discover more about different authentication techniques and approaches on the authentication overview page. In the sections ahead, you'll learn:
A managed identity enables your app to securely connect to other Azure resources without the use of secret keys or other application secrets. Internally, Azure tracks the identity and which resources it's allowed to connect to. Azure uses this information to automatically obtain Microsoft Entra tokens for the app to allow it to connect to other Azure resources.
There are two types of managed identities to consider when configuring your hosted app:
Tip
Learn more about selecting and managing system-assigned managed identities and user-assigned managed identities in the Managed identity best practice recommendations article.
The sections ahead describe the steps to enable and use a user-assigned managed identity for an Azure-hosted app. If you need to use a user-assigned managed identity, visit the system-assigned managed identities article for more information.
User-assigned managed identities are created as standalone resources in your Azure subscription using the Azure portal or the Azure CLI. Azure CLI commands can be run in the Azure Cloud Shell or on a workstation with the Azure CLI installed.
In the Azure portal, enter Managed identities in the main search bar and select the matching result under the Services section.
On the Managed Identities page, select + Create.

On the Create User Assigned Managed Identity page, select a subscription, resource group, and region for the user-assigned managed identity, and then provide a name.
Select Review + create to review and validate your inputs.

Select Create to create the user-assigned managed identity.
After the identity is created, select Go to resource.
On the new identity's Overview page, copy the Client ID value to use for later when you configure the application code.
A user-assigned managed identity can be associated with one or more Azure resources. All of the resources that use that identity gain the permissions applied through the identity's roles.
In the Azure portal, navigate to the resource that hosts your app code, such as an Azure App Service or Azure Container App instance.
From the resource's Overview page, expand Settings and select Identity from the navigation.
On the Identity page, switch to the User assigned tab.
Select + Add to open the Add user assigned managed identity panel.
On the Add user assigned managed identity panel, use the Subscription dropdown to filter the search results for your identities. Use the User assigned managed identities search box to locate the user-assigned managed identity you enabled for the Azure resource hosting your app.
Select the identity and choose Add at the bottom of the panel to continue.

Next, determine which roles your app needs and assign those roles to the managed identity. You can assign roles to a managed identity at the following scopes:
The following example shows how to assign roles at the resource group scope, since many apps manage all their related Azure resources using a single resource group.
Navigate to the Overview page of the resource group that contains the app with the user-assigned managed identity.
Select Access control (IAM) on the left navigation.
On the Access control (IAM) page, select + Add on the top menu and then choose Add role assignment to navigate to the Add role assignment page.
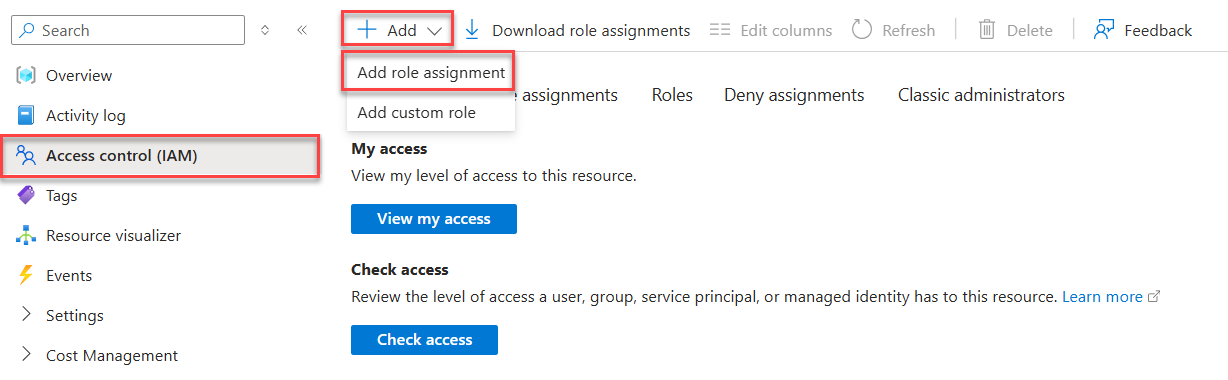
The Add role assignment page presents a tabbed, multi-step workflow to assign roles to identities. On the initial Role tab, use the search box at the top to locate the role you want to assign to the identity.
Select the role from the results and then choose Next to move to the Members tab.
For the Assign access to option, select Managed identity.
For the Members option, choose + Select members to open the Select managed identities panel.
On the Select managed identities panel, use the Subscription and Managed identity dropdowns to filter the search results for your identities. Use the Select search box to locate the user-assigned managed identity you enabled for the Azure resource hosting your app.

Select the identity and choose Select at the bottom of the panel to continue.
Select Review + assign at the bottom of the page.
On the final Review + assign tab, select Review + assign to complete the workflow.
The Azure Identity library provides various credentials—implementations of TokenCredential adapted to supporting different scenarios and Microsoft Entra authentication flows. Since managed identity is unavailable when running locally, the steps ahead demonstrate which credential to use in which scenario:
DefaultAzureCredential discovers user credentials from your local tooling or IDE, such as the Azure CLI or Visual Studio. It also provides flexibility and convenience for retries, wait times for responses, and support for multiple authentication options. Visit the Authenticate to Azure services during local development article to learn more.Add the Azure.Identity package. In an ASP.NET Core project, also install the Microsoft.Extensions.Azure package:
In a terminal of your choice, navigate to the application project directory and run the following commands:
dotnet add package Azure.Identity
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Azure
Azure services are accessed using specialized client classes from the various Azure SDK client libraries. These classes and your own custom services should be registered for dependency injection so they can be used throughout your app. In Program.cs, complete the following steps to configure a client class for dependency injection and token-based authentication:
Azure.Identity and Microsoft.Extensions.Azure namespaces via using directives.Add-prefixed extension method.TokenCredential instance to the UseCredential method:
DefaultAzureCredential when your app is running locallyManagedIdentityCredential when your app is running in Azure and configure either the client ID, resource ID, or object ID.The client ID is used to identify a managed identity when configuring applications or services that need to authenticate using that identity.
Retrieve the client ID assigned to a user-assigned managed identity using the following command:
az identity show \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--name <identity-name> \
--query 'clientId'
Configure ManagedIdentityCredential with the client ID:
builder.Services.AddAzureClients(clientBuilder =>
{
clientBuilder.AddBlobServiceClient(
new Uri("https://<account-name>.blob.core.windows.net"));
TokenCredential credential = null;
if (builder.Environment.IsProduction() || builder.Environment.IsStaging())
{
// Managed identity token credential discovered when running in Azure environments
credential = new ManagedIdentityCredential(
ManagedIdentityId.FromUserAssignedClientId("<client-id>"));
}
else
{
// Running locally on dev machine - DO NOT use in production or outside of local dev
credential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
}
clientBuilder.UseCredential(credential);
});
An alternative to the UseCredential method is to provide the credential to the service client directly:
TokenCredential credential = null;
if (builder.Environment.IsProduction() || builder.Environment.IsStaging())
{
// Managed identity token credential discovered when running in Azure environments
credential = new ManagedIdentityCredential(
ManagedIdentityId.FromUserAssignedClientId("<client-id>"));
}
else
{
// Running locally on dev machine - DO NOT use in production or outside of local dev
credential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
}
builder.Services.AddSingleton<BlobServiceClient>(_ =>
new BlobServiceClient(
new Uri("https://<account-name>.blob.core.windows.net"), credential));
The preceding code behaves differently depending on the environment where it's running:
DefaultAzureCredential looks in the environment variables for an application service principal or at locally installed developer tools, such as Visual Studio, for a set of developer credentials.ManagedIdentityCredential discovers your managed identity configurations to authenticate to other services automatically..NET feedback
.NET is an open source project. Select a link to provide feedback:
Events
Mar 17, 9 PM - Mar 21, 10 AM
Join the meetup series to build scalable AI solutions based on real-world use cases with fellow developers and experts.
Register nowTraining
Module
Introduction to using Managed Identity to authenticate to Azure OpenAI with .NET - Training
How to implement role based access control and managed identity authentication to Azure OpenAI with .NET.
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Identity and Access Administrator Associate - Certifications
Demonstrate the features of Microsoft Entra ID to modernize identity solutions, implement hybrid solutions, and implement identity governance.