Microsoft Azure Attestation troubleshooting guide
Error handling in Azure Attestation is implemented following Microsoft REST API guidelines. The error response returned by Azure Attestation APIs contains HTTP status code and name/value pairs with the names "code" and "message". The value of "code" is human-readable and is an indicator of the type of error. The value of "message" intends to aid the user and provides error details.
If your issue isn't addressed in this article, you can also submit an Azure support request on the Azure support page.
HTTP–401: Unauthorized exception
HTTP status code
401
Error code Unauthorized
Scenario examples
- Unable to manage attestation policies as the user isn't assigned with appropriate roles
- Unable to manage attestation policy signers as the user isn't assigned with appropriate roles
User with Reader role trying to edit an attestation policy in PowerShell
Set-AzAttestationPolicy : Operation returned HTTP Status Code 401
At line:1 char:1
+ Set-AzAttestationPolicy -Name $attestationProvider -ResourceGroupName ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Set-AzAttestationPolicy], RestException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Attestation.SetAzureAttestationPolicy
Troubleshooting steps
In order to manage policies, a Microsoft Entra user requires the following permissions for "Actions":
Microsoft.Attestation/attestationProviders/attestation/read
Microsoft.Attestation/attestationProviders/attestation/write
Microsoft.Attestation/attestationProviders/attestation/delete
To perform these actions, a Microsoft Entra user must have "Attestation Contributor" role on the attestation provider. These permissions can also be inherited with roles such as "Owner" (wildcard permissions), "Contributor" (wildcard permissions) on the subscription/ resource group.
In order to read policies, a Microsoft Entra user requires the following permission for "Actions":
Microsoft.Attestation/attestationProviders/attestation/read
To perform this action, a Microsoft Entra user must have "Attestation Reader" role on the attestation provider. Read permissions are also part of roles such as "Reader" (wildcard permissions) on the subscription/ resource group.
To verify the roles in PowerShell, run the below steps:
a. Launch PowerShell and log into Azure via the "Connect-AzAccount" cmdlet
b. Refer to the guidance here to verify your Azure role assignment on the attestation provider
c. If you don't find an appropriate role assignment, follow the instructions in here
HTTP – 400 errors
HTTP status code
400
There are different reasons why a request may return 400. Here are some examples of errors returned by Azure Attestation APIs.
Attestation failure due to policy evaluation errors
Attestation policy includes authorization rules and issuance rules. Enclave evidence is evaluated based on the authorization rules. Issuance rules define the claims to be included in attestation token. If claims in enclave evidence don't comply with authorization rules, attest calls will return policy evaluation error.
Error code PolicyEvaluationError
Scenario examples When claims in the enclave quote don't match with the authorization rules of attestation policy
Native operation failed with 65518: G:\Az\security\Attestation\src\AttestationServices\Instance\NativePolicyWrapper\NativePolicyEngine.cpp(168)\(null)!00007FF801762308: (caller: 00007FF80143DCC8) Exception(0) 83FFFFEE Policy Evaluation Error has occurred Msg:[Policy Engine Exception: A Deny claim was issued, authorization failed.]
G:\Az\security\Attestation\src\AttestationServices\Instance\Enclave\api.cpp(840)\(null)!00007FF801739FF3: (caller: 00007FF801232801) LogHr(0) 83FFFFEE Policy Evaluation Error has occurred Msg:[Unhandled Enclave Exception: "Policy Evaluation Error has occurred"]
Troubleshooting steps Users can evaluate enclave evidence against an SGX attestation policy before configuring the same.
Send a request to attest API by providing policy text in "draftPolicyForAttestation" parameter. The AttestSgxEnclave API will use this policy document during the attest call and this can be used to test attestation policies before they are consumed. The attestation token generated when this field is present will be unsecured.
See attestation policy examples
Attestation failure due to invalid input
Error code InvalidParameter
Scenario examples SGX attestation failure due to invalid input. Here are some examples of error messages:
- The specified quote was invalid due to an error in the quote collateral
- The specified quote was invalid because the device on which the quote was generated does not meet the Azure baseline requirements
- The specified quote was invalid because the TCBInfo or QEID provided by the PCK Cache Service was invalid
Troubleshooting steps
Microsoft Azure Attestation supports attestation of SGX quotes generated by Intel SDK and Open Enclave SDK.
Refer to code samples for performing attestation using Open Enclave SDK/ Intel SDK
Invalid certificate chain error while uploading policy/policy signer
Error code InvalidParameter
Scenario examples Configure signed policy or add/delete policy signer, which is signed with an invalid certificate chain (for example, when the Basic Constraints extension of the root certificate is not set to Subject Type = CA)
Native operation failed with 65529: C:\source\src\AttestationServices\Instance\SgxPal\sgxcert.cpp(1074)\(null)!00007FFA285CDAED: (caller: 00007FFA285C36E8) Exception(0) 83FFFFF9 The requested item is not found Msg:[Unable to find issuer certificate CN=attestationsigningcert]
C:\source\src\AttestationServices\Instance\Enclave\api.cpp(618)\(null)!00007FFA286DCBF8: (caller: 00007FFA285860D3) LogHr(0) 83FFFFF9 The requested item is not found Msg:[Unhandled Enclave Exception: "The requested item is not found"]
At line:1 char:1
+ Set-AzAttestationPolicy -Name "testpolicy1" -ResourceGroupName "BugBa ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Set-AzAttestationPolicy], RestException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Attestation.SetAzureAttestationPolicy
Troubleshooting steps The root certificate must be flagged as being issued by a CA (the X.509 basic constraints), else it will not be considered as a valid certificate.
Ensure that the Basic Constraints extension of the root certificate is set to indicate that Subject Type = CA
Else the certificate chain is considered to be invalid.
See policy signer and policy examples
Add/Delete policy signer failure
Error code InvalidOperation
Scenario examples
When user uploads JWS without "maa-policyCertificate" claim
Add-AzAttestationPolicySigner : Operation returned HTTP Status Code 400
Code: InvalidOperation
Message: Native operation failed with 74: ..\Enclave\enclave.cpp(2213)\(null)!: (caller: ) Exception(0) 83FF004A Bad
message Msg:[Could not find "maa-policyCertificate" claim in policy token]
..\Enclave\api.cpp(496)\(null)!: (caller: ) LogHr(0) 83FF004A Bad message Msg:[Unhandled Enclave Exception: "Bad
message"]
At line:1 char:1
+ Add-AzAttestationPolicySigner -Name $attestationProvider -ResourceGro ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Add-AzAttestationPolicySigner], RestException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Attestation.AddAzureAttestationPolicySigner
When user does not upload a certificate in JWS format
Add-AzAttestationPolicySigner : Operation returned HTTP Status Code 400
Code: InvalidOperation
Message: Native operation failed with 74: ..\JsonWebToken\jsonwebtoken.cpp(375)\(null)!: (caller: ) LogHr(0) 83FF004A
Bad message Msg:[RETURN_IF_TRUE('(firstPeriod == std::string::npos)') failed with 0x4a: Malformed JWT: Could not
find first period in the token.]
..\Enclave\enclave.cpp(2106)\(null)!: (caller: ) LogHr(0) 83FF004A Bad message
Msg:[THROW_IF_ERROR('DecomposeJsonWebSignature(&policyJws, encodedJoseHeader, encodedJwsBody, jwsSignature)') failed
with 0x4a: 'Bad message']
..\Enclave\enclave.cpp(2106)\(null)!: (caller: ) Exception(0) 83FF004A Bad message
..\Enclave\api.cpp(496)\(null)!: (caller: ) LogHr(0) 83FF004A Bad message Msg:[Unhandled Enclave Exception: "Bad
message"]
At line:1 char:1
+ Add-AzAttestationPolicySigner -Name $attestationProvider -ResourceGro ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Add-AzAttestationPolicySigner], RestException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Attestation.AddAzureAttestationPolicySigner
Troubleshooting steps To add/delete a new policy signer certificate, use RFC7519 JSON Web Token (JWT) with a claim named "x-ms-policyCertificate". Value of the claim is an RFC7517 JSON Web Key, which contains the certificate to be added. JWT must be signed with private key of any of the valid policy signer certificates associated with the provider. See policy signer examples.
Attestation policy configuration failure
Error code PolicyParsingError
Scenario examples Policy provided with incorrect syntax (for example, missing semicolon)/valid JWT policy)
Native operation failed with 65526: ..\NativePolicyWrapper\NativePolicyEngine.cpp(31)\(null)!: (caller: ) Exception(0) 83FFFFF6 Invalid policy was specified Msg:[Policy Parser Exception Thrown: Offending
symbol: '['
Line: '2', Column: '1'
Failure message: 'mismatched input '[' expecting ';''
Failing rule: 'policy > versionInfo']
..\Enclave\api.cpp(618)\(null)!: (caller: ) LogHr(0) 83FFFFF6 Invalid policy was specified Msg:[Unhandled Enclave Exception: "Invalid policy was specified"]
At line:1 char:1
+ set-AzAttestationPolicy -Name $attestationProvider -ResourceGroupName ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Set-AzAttestationPolicy], RestException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Attestation.SetAzureAttestationPolicy
Error code InvalidOperation
Scenario examples Invalid content provided (for example, upload policy/ unsigned policy when policy signing is required)
Native operation failed with 74: ..\Shared\base64url.h(226)\(null)!: (caller: ) Exception(0) 83FF004A Bad message Msg:[Unknown base64 character: 41 (')')]
..\Enclave\api.cpp(618)\(null)!: (caller: ) LogHr(0) 83FF004A Bad message Msg:[Unhandled Enclave Exception: "Bad message"]
At line:1 char:1
+ set-AzAttestationPolicy -Name $attestationProvider -ResourceGroupName ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : CloseError: (:) [Set-AzAttestationPolicy], RestException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Attestation.SetAzureAttestationPolicy
Troubleshooting steps Ensure that the policy in Text format is UTF-8 encoded.
If policy signing is required, attestation policy must be configured only in RFC7519 JSON Web Token (JWT) format. If policy signing is not required, policy can be configured in text or JWT format.
To configure a policy in JWT format, use JWT with a claim named "AttestationPolicy". Value of the claim is Base64URL encoded version of the policy text. If the attestation provider is configured with policy signer certificates, the JWT must be signed with private key of any of the valid policy signer certificates associated with the provider.
To configure a policy in text format, specify policy text directly.
In PowerShell, specify PolicyFormat as JWT to configure policy in JWT format. Default policy format is Text.
See attestation policy examples and how to author an attestation policy
Az.Attestation installation issues in PowerShell
Unable to install the Az PowerShell module or Az.Attestation PowerShell module in PowerShell.
Error
WARNING: Unable to resolve package source 'https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2' PackageManagement\Install-Package: No match was found for the specified search criteria and module name
Troubleshooting steps
PowerShell Gallery has deprecated Transport Layer Security (TLS) versions 1.0 and 1.1.
TLS 1.2 or a later version is recommended.
To continue to interact with the PowerShell Gallery, run the following command before the Install-Module commands
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Policy access/configuration issues in PowerShell
User assigned with appropriate roles. But facing authorization issues while managing attestation policies through PowerShell.
Error
The client with object ID <object Id> does not have authorization to perform action Microsoft.Authorization/roleassignments/write over scope ‘subcriptions/<subscriptionId>resourcegroups/secure_enclave_poc/providers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleassignments/<role assignmentId>’ or the scope is invalid. If access was recently granted, refresh your credentials
Troubleshooting steps
The minimum version of the Az PowerShell modules required to support attestation operations are:
- Az 4.5.0
- Az.Accounts 1.9.2
- Az.Attestation 0.1.8
Run the below command to verify the installed version of all Az modules
Get-InstalledModule
If the versions do not meet the minimum requirement, run the Update-Module PowerShell cmdlet.
Update-Module -Name Az.Attestation
Installation issues with Guest Attestation extension
This section addresses attestation errors and solutions.
Symptoms
The Azure Attestation extension won't work properly when you set up a network security group (NSG) or a proxy. An error appears that looks similar to "Microsoft.Azure.Security.WindowsAttestation.GuestAttestation provisioning failed."
Solutions
In Azure, NSGs are used to help filter network traffic between Azure resources. NSGs contain security rules that either allow or deny inbound network traffic, or outbound network traffic from several types of Azure resources. The Azure Attestation endpoint should be able to communicate with the Guest Attestation extension. Without this endpoint, Trusted Launch can't access guest attestation, which allows Microsoft Defender for Cloud to monitor the integrity of the boot sequence of your VMs.
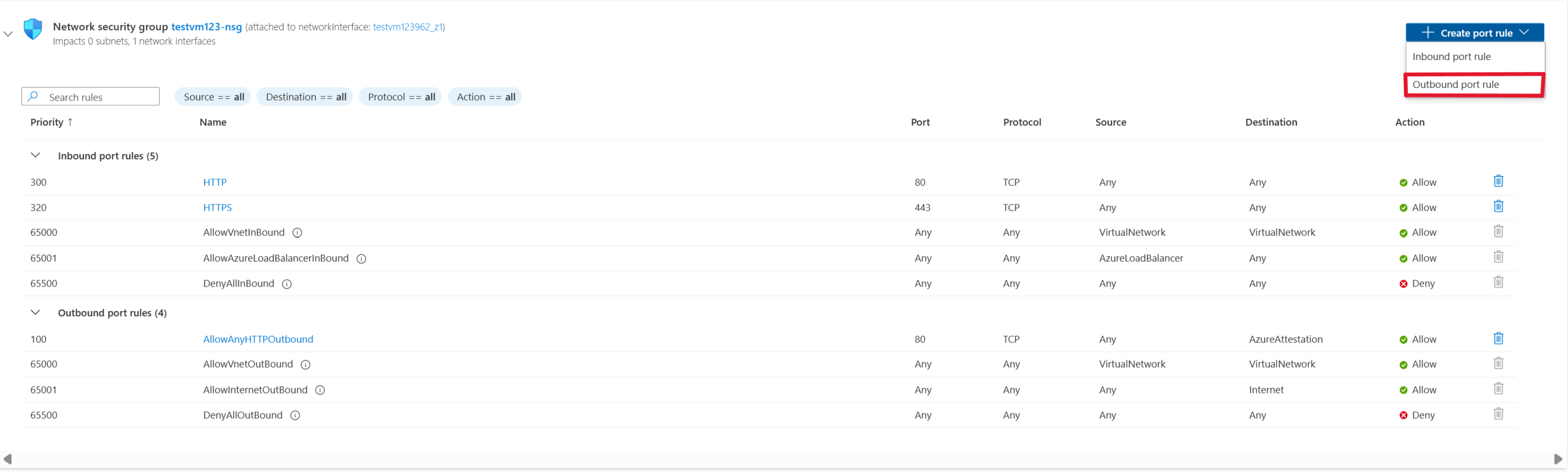
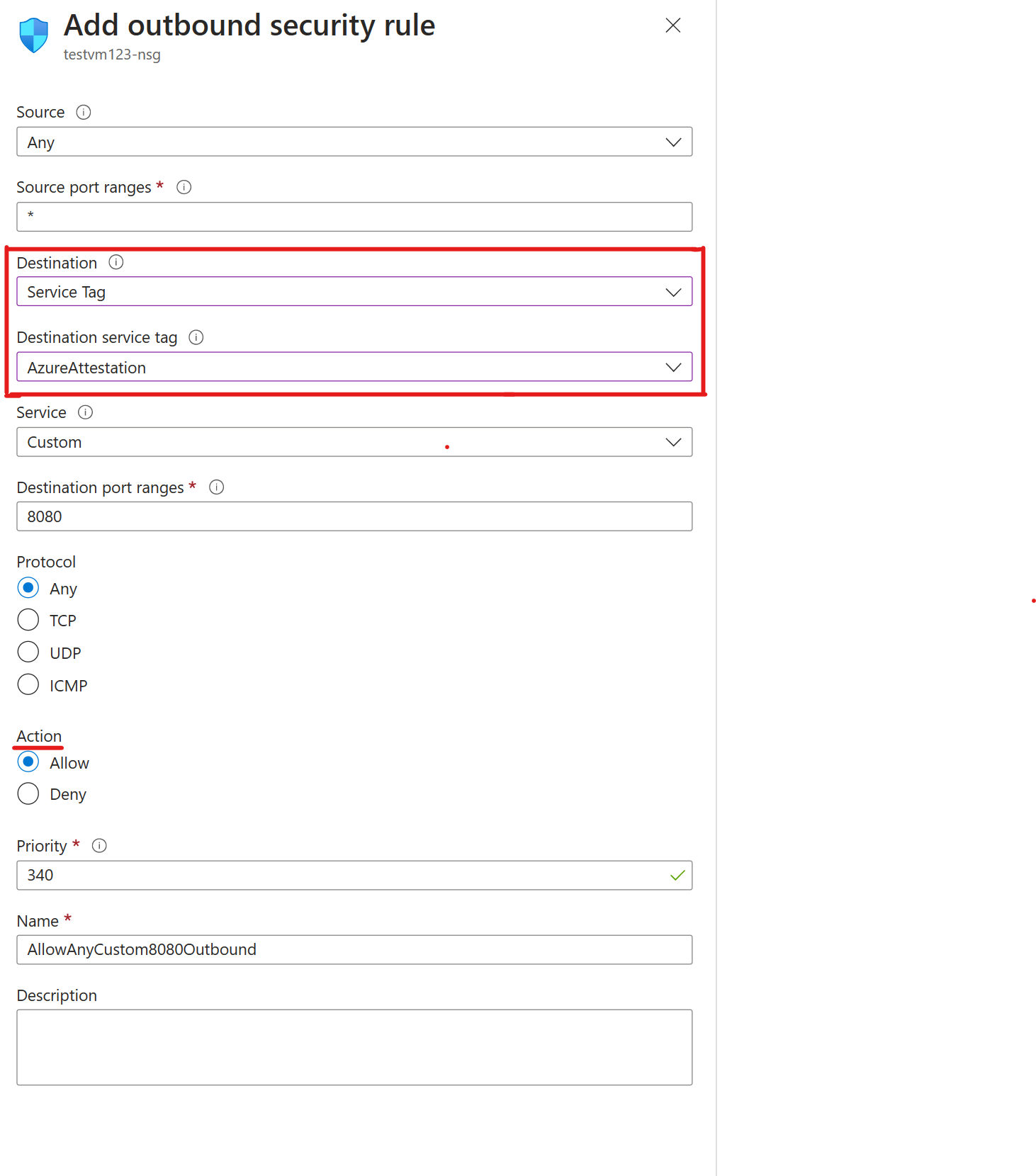
To unblock Azure Attestation traffic in NSGs by using service tags:
Go to the VM that you want to allow outbound traffic.
On the leftmost pane, under Networking, select Networking settings.
Then select Create port rule > Outbound port rule.
To allow Azure Attestation, you make the destination a service tag. This setting allows for the range of IP addresses to update and automatically set rules that allow Azure Attestation. Set Destination service tag to AzureAttestation and set Action to Allow.
Firewalls protect a virtual network, which contains multiple Trusted Launch VMs. To unblock Azure Attestation traffic in a firewall by using an application rule collection:
Go to the Azure Firewall instance that has traffic blocked from the Trusted Launch VM resource.
Under Settings, select Rules (classic) to begin unblocking guest attestation behind the firewall.
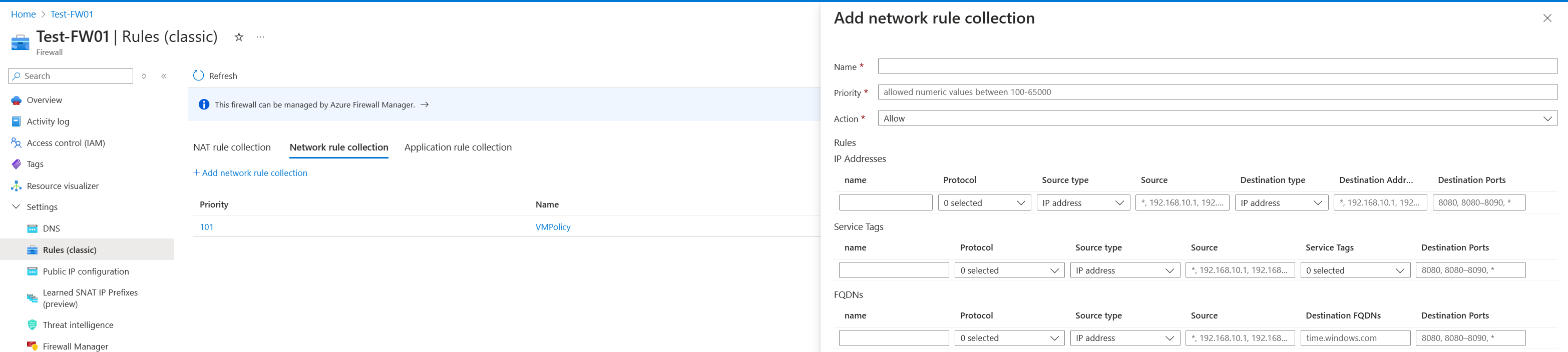
Under Network rule collection, select Add network rule collection.
Configure the name, priority, source type, and destination ports based on your needs. Set Service tag name to AzureAttestation and set Action to Allow.
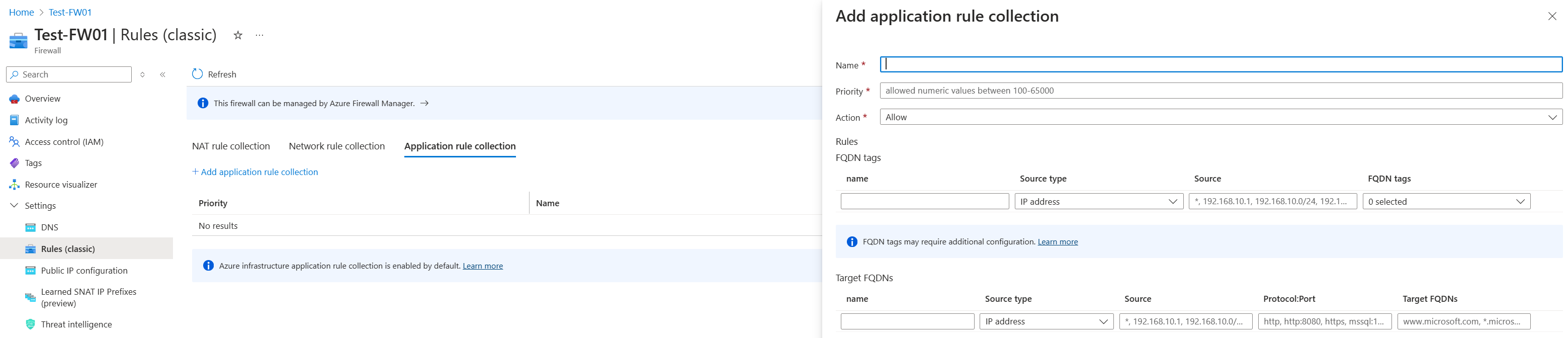
To unblock Azure Attestation traffic in a firewall by using an application rule collection:
Go to the Azure Firewall instance that has traffic blocked from the Trusted Launch VM resource.
The rules collection must contain at least one rule that targets fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
Select the application rule collection and add an application rule.
Select a name and a numeric priority for your application rules. Set Action for the rule collection to Allow.
Configure the name, source, and protocol. The source type is for a single IP address. Select the IP group to allow multiple IP addresses through the firewall.